- Table of Contents
- Intro
- When It Matters
- Our Tests
- Conclusion
- Comments
- 10.0% Audio Format Support: ARC/eARC
- 10.0% Audio Format Support: HDMI In
- 10.0% Audio Format Support: Optical
- 1.0% Audio Latency: ARC
- 1.0% Audio Latency: HDMI In
- 1.0% Audio Latency: Optical
- 1.0% Video Passthrough To TV
- 10.0% Wireless Playback
Whether you like listening to music or watching movies and TV shows, soundbars are a great way to create an immersive listening experience in your home. However, to listen to your audio, you'll need to connect your soundbar to an audio source like a TV, PC, or gaming console. Our connectivity tests evaluate the physical inputs available and any wireless playback options like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Depending on the media sources you plan to use and the type of media you like to listen to, you may prefer a soundbar with certain connectivity options.
We test several different factors to evaluate a soundbar's connectivity performance, including audio format support and latency via ARC, Full HDMI In, and Optical, wireless playback, and video passthrough capabilities. We also list the inputs and outputs that are available.
Test results
When It Matters
Your personal preferences are important for understanding the connectivity options you'll want from your soundbar since they'll determine the type of media devices you'll want to connect it with. You may want to look at the connectivity options available on your TV as well as any other media devices you plan to connect to your soundbar, like Blu-ray players, PCs, or gaming consoles. The type of audio content you like to listen to also plays a role in the connectivity options you'll want out of your soundbar. You may prefer to watch certain surround sound movie formats like Dolby Digital or DTS:X, or you may only want to play music from your smartphone.
Our Tests
To evaluate a soundbar's connectivity options, we perform a variety of tests. While we can look at the bar to see which physical inputs and outputs it offers, we also test its performance over some of those inputs to see which audio formats are supported and the amount of latency over these connections. We also look at the wireless playback options that the bar supports. If there's a Full HDMI In port available, we also test to see if it has video passthrough capabilities.
You can find more information about how we perform each test below.
Inputs/Outputs - Bar
If you want to connect your soundbar to your gaming console, PC, TV, and more, you'll want to see which physical inputs and outputs are available. Most soundbars we've tested have HDMI ARC and Optical In ports, commonly used to connect the soundbar to your TV. However, a Full HDMI In port can also be helpful since it allows you to passthrough video and use your bar as a hub between different devices. You may also want to get your audio from other sources like older devices or USB drives, so other ports like AUX In or USB In may be important. We also look to see whether there's an output to connect an external subwoofer over a wired connection.


Audio Format Support - ARC
- 1.0% Dolby Atmos
- 4.5% Dolby Digital
- 1.0% Dolby Digital Plus
- 1.0% Dolby TrueHD
- 1.5% DTS
- 0.2% DTS:X
- 0.2% DTS-HD MA
- 0.6% PCM Channels
If you want to connect your soundbar to your TV, you'll probably want to use an HDMI ARC or eARC connection. After all, HDMI ARC has more features than optical, with higher bandwidth for streaming more advanced audio formats like Dolby Atmos. Also, HDMI ARC enables two-way data transmission, meaning you can use the port as both an input and an output simultaneously. You can learn more about the difference between HDMI and Optical, as well as ARC and eARC, here.
Before you press play, you'll want to ensure that it supports the audio formats you like to watch. Many soundbars with HDMI indeed advertise support for particular audio formats like Dolby Digital and Dolby Atmos. While a bar might be able to play some sound, that doesn't mean that it's playing the format correctly. These audio formats are designed to provide an immersive feel by allocating specific sound effects to specific channels—so, for example, a helicopter flying overhead on-screen sounds like it's flying overhead in your living room. If the bar doesn't play those effects on the right channels, you don't get the same all-around feel.
For our tests, we've designed our own Blu-ray discs to ensure that each audio file used in our testing is reliable. We encoded these discs using files available on both Dolby Media Encoder and Demolandia. We've also confirmed that each disc is properly encoded using MPC-HC, an open-source media player for Windows that supports all common video and audio formats. Each channel played back correctly through the media player, so we know any issues encountered in testing are specific to the bar and not the audio file itself.
From there, it's simple. We connect the soundbar to a Blu-ray player and attempt each of the audio file formats. Each disc plays out a callback test, in which a voice "calls out" each of the channels, one after the other. That way, we can confirm that sound comes from that channel and only that channel. You can see an example in the embedded video.
Our final results are divided into three categories. "Supported" confirms that the audio file plays back on each channel as intended by the original audio engineers. "Incorrect Implementation" lets us elaborate on anything unusual we encounter in our tests—for example, if a sound meant for one channel plays on another simultaneously or doesn't play at all. We'll also note if a format is "Not Supported" at all.
Audio Format Support - Full HDMI In
- 1.0% Dolby Atmos
- 4.5% Dolby Digital
- 1.0% Dolby Digital Plus
- 1.0% Dolby TrueHD
- 1.5% DTS
- 0.2% DTS:X
- 0.2% DTS-HD MA
- 0.6% PCM Channels
As its name implies, HDMI In ports are designed to input sound. They're especially useful if you want to passthrough video from a gaming console or Blu-ray player to your TV while playing audio through your soundbar. Essentially, you can use the bar as a "hub" between different devices, connecting it to your TV via ARC and to your second device via HDMI In.
For these tests, we rely on the same methodology as our ARC tests. We use Blu-rays encoded with specific audio formats to confirm whether the bar receives this content properly over HDMI In and note any instances of incorrect implementation within the text itself.
Audio Format Support - Optical
- 4.5% Dolby Digital
- 3.5% DTS
- 2.0% PCM Channels
Optical is also known as Toslink or S/PDIF. It's another connectivity option available to connect your TV with most soundbars, though it offers fewer features than HDMI or ARC. Still, it's a decent fallback when the other options aren't available, which may be the case if you're trying to connect the soundbar to an older TV model. You can learn more about the differences between HDMI and Optical in our article here.
Our audio format support tests for Optical follow the same methodology as HDMI and ARC.
Audio Latency: ARC
- 4.5% PCM-2.0 ch
- 4.5% PCM-5.1 ch
- 12.0% Dolby MAT (PCM) Atmos
- 55.0% Dolby Digital
- 12.0% Dolby Digital Plus
- 12.0% Dolby Digital Plus Atmos
High amounts of latency take away from the immersive feel of your favorite movies, TV shows, and video games, especially when you notice obvious lip-synching errors. Our tests are designed to measure audio latency, also known as the delay between when an audio signal is inputted and when that audio plays through the soundbar's speakers. Audio latency can vary depending on the audio format you play, so we test various formats with each connection.
Audio latency is only one part of the equation regarding noticeable delay on your TV screen. After all, the display you use will impact the video latency or the delay between when a video signal is inputted and when it shows on your screen. We can't test for every display on the market, so we use our videos to approximate what you'll experience in real life. You can get a sense of what low AV synchronization error looks like, as well as what it looks like on the higher end. Since many TVs synchronize their ARC/eARC audio and video output, you'll want an audio latency result that's as close to 0 ms as possible.
Our article on our latency tests dives more in-depth into our testing process and the philosophy behind our recorded videos. If you're interested in learning more about these tests over any of the three connection types, it's worth a look.
Audio Latency: HDMI In
- 4.5% PCM-2.0 ch
- 4.5% PCM-5.1 ch
- 12.0% Dolby MAT (PCM) Atmos
- 55.0% Dolby Digital
- 12.0% Dolby Digital Plus
- 12.0% Dolby Digital Plus Atmos
The connection type you use impacts audio latency. While most users will want to connect their bar to their TV over an ARC connection, you may want to use HDMI In for video passthrough instead. In that case, you'll want to look at your soundbar's audio latency performance over HDMI In. Again, we test with a variety of common audio formats like Dolby Digital to give you a better sense of what to expect in your particular use.
Ideally, the audio latency over HDMI In matches the video latency of your display. If you don't know how your display performs, you can always look at our videos to get an approximation with both low and high AV synchronization error. Some soundbars also have features to manually adjust the delay, which can be handy if you experience any lip-synching issues.
Audio Latency: Optical
- 70.0% PCM-2.0 ch
- 30.0% Dolby Digital
Optical is a handy fallback for those whose TVs don't support HDMI connectivity. You'll get access to fewer audio formats over this connection, though we still test for Dolby Digital and PCM 2.0 content. Again, you'll want the audio latency to match the video latency of your display. Our video approximates the AV synchronization error on both the high and low ends of the spectrum to give you a better sense of what you'll experience in real life.
Video Passthrough To TV
- 30.0% 1080p Max Refresh Rate
- 15.0% 1080p @ 4:4:4 Max Refresh Rate
- 20.0% 4k Max Refresh Rate
- 5.0% 4k @ 120Hz @ 10-Bit
- 5.0% 4k @ 4:4:4 Max Refresh Rate
- 5.0% 8k Max Refresh Rate
- 5.0% HDR10 Passthrough
- 2.0% HDR10+ Passthrough
- 5.0% Dolby Vision Passthrough
- 3.0% HDMI Forum VRR Passthrough
- 2.0% FreeSync Passthrough
- 1.0% G-SYNC Passthrough
- 2.0% ALLM Passthrough
If you like to use your soundbar as a hub between different devices, you may want a soundbar that supports high-quality passthrough. Some soundbars support video passthrough, which lets you connect a media device like a PC or Blu-ray player to the soundbar and then connect the soundbar to your TV without losing video resolution. As a result, images on your TV look vivid and bright, and text appears clear and crisp. The audio on the soundbar will be clear, too, and you'll have fewer cables to manage. You can see an example of this setup in the image below, and you can also learn more about how it all works in the article here.
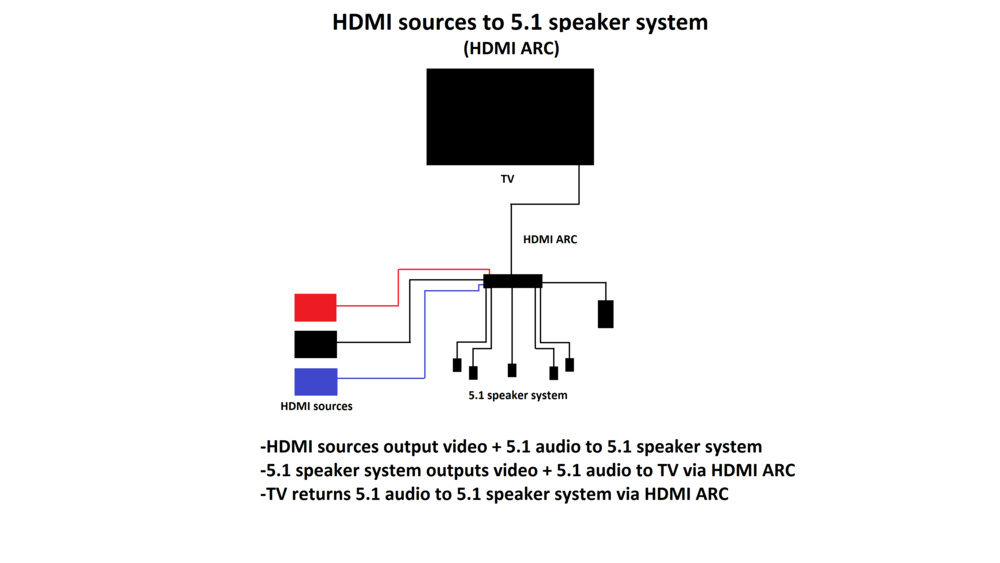
Our tests are focused on the most common TV resolutions and refresh rates using a Murideo Seven Generator for confirmation. The Murideo allows us to check for HDR10 and Dolby Vision, while we use an Apple TV 4k 3rd Gen to test for HDR10+. All these technologies are becoming more common on Blu-rays and streaming platforms. You can learn more about where to find 4k and HDR content here.
Our 4k @ 120Hz @ 10-bit comparison also serves as a confirmation for whether the bar supports HDMI 2.1 Class Bandwidth since HDMI 2.0 only has the bandwidth to support 4k @ 120Hz @ 8-bit.
Finally, we examine whether the bar supports different variable refresh rate (VRR) technologies. An Xbox One X allows us to test for HDMI Forum VRR and FreeSync. We also use a PS5 to check for HDMI Forum VRR, as well as a PC with an NVIDIA Series 1000 card to evaluate G-SYNC. Both the PS5 and the Xbox One X are used to check for ALLM. Depending on your console, you'll want to check for certain VRR rates over others since they don't all support the same ones. Notably, VRR is included with the new HDMI 2.1 standard. Since it's all relatively new, you can also look out for NVIDIA's G-SYNC and AMD's FreeSync.
Wireless Playback
- 60.0% Bluetooth
- 20.0% Wi-Fi Playback
- 10.0% Chromecast built-in
- 10.0% Apple AirPlay
Mobile devices like smartphones and tablets are convenient locations to store audio content like music, podcasts, and audiobooks. You may be able to wire some of these devices to your soundbar for audio playback, but many listeners find it more convenient to connect wirelessly. For this test, we look to see if the bar supports Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Chromecast built-in, Spotify Connect, and Apple AirPlay, some of the more common wireless playback options on the market. Bluetooth can be especially useful since it doesn't require an internet connection. However, your device may offer other connectivity options depending on the brand, like Apple's AirPlay or Google's Chromecast built-in. It's important to remember that we don't test the performance of the wireless playback options, and we only report what the soundbar supports.
Conclusion
If you want to listen to audio on your soundbar, you'll want to make sure you can connect it to the audio source of your choice. Our connectivity tests look to see which physical and wireless inputs are available for audio playback. We also evaluate the performance of some of the most common physical inputs, including ARC, Full HDMI In, and Optical, to see which audio formats they support and whether they have low latency. Depending on how you want to use your soundbar, you may want a soundbar with certain connectivity options.