LED TVs are one of the most popular types of TV on the market. But what is LED, and should you consider one for your next TV purchase? In this article, we'll break down some of the history of LED TVs, their benefits, and when you should consider one. If you've already made your decision and you're ready to pick a specific model, check out our list of the best LED LCD TVs. If you're not sure if LED is right for you, our TV panel type overview guide is a great place to start.
What Is LED?

Simply put, an LED TV is an LCD TV that uses LEDs as a backlight. Okay, so what is LCD? LCD stands for liquid crystal display, and it refers to how this type of TV controls the flow of light. LCDs have been around for a very long time, but the first versions of these TVs used cold-cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) as a light source. These lamps had a lot of downsides. They were bulky, they had a relatively limited life span, and they used mercury, which posed health risks if they broke. TV manufacturers started switching to LED backlights in the mid-2000s, and they grew in popularity very quickly. LEDs are thin, they last longer than CCFLs, and they're significantly more energy-efficient.
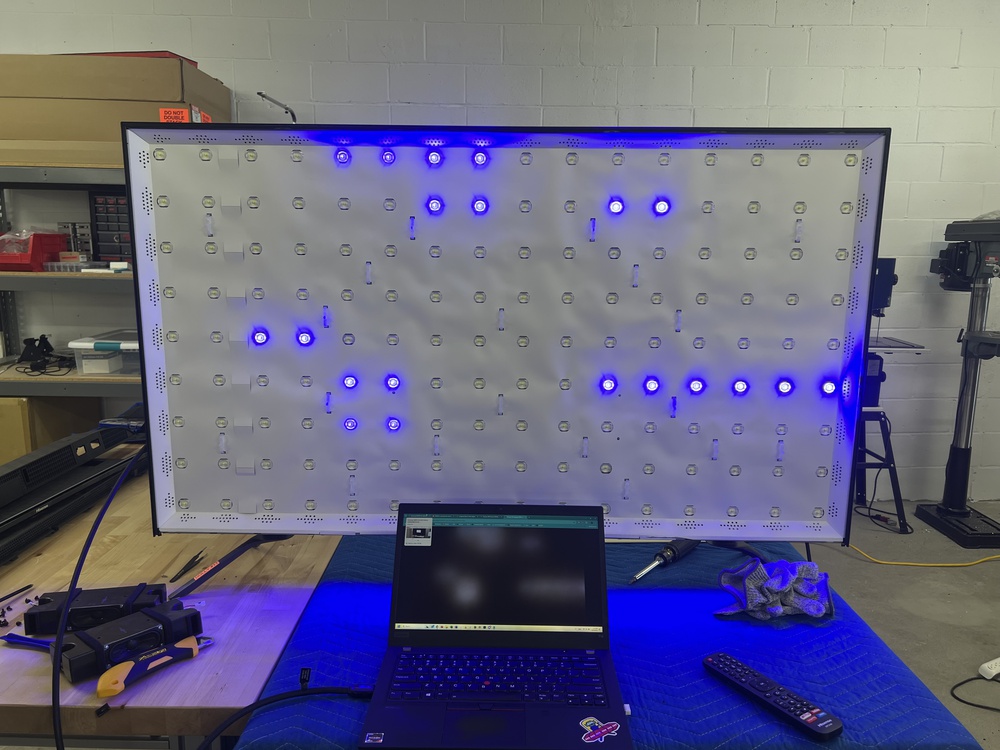
Although LED TVs have been out for over 20 years now, not much has changed. They've gotten smaller, brighter, and more energy-efficient, but the underlying technology is basically the same. Modern LED TVs still rely on LCD panels to actually display an image, so the terms LED and LCD are often used interchangeably. You can see an example of an LED array above. Blue LEDs are arranged in a grid, which is one of the first stacks in the overall TV structure. The light from the LEDs passes through various layers, including the LCD layer, which acts similarly to the iris of a camera, controlling the flow of light from the backlight through the colored layers that make up the subpixels. There are different types of LCD panels, including IPS, ADS, and VA. We refer to these as the subtypes of an LED TV.
LED Performance
LED TVs come in many different shapes and sizes. In fact, that's one of their greatest strengths. From tiny displays on home appliances and electronics up to the largest TVs on the market, LED/LCD displays can be found everywhere. So how do they perform? To better understand what to expect, we'll look at the overall spread and median results for a few key performance indicators: contrast, brightness, color volume, and motion blur. We'll look at some of the key results of the 55 LED/LCD TVs we've tested on either our 2.0.1 or 2.1 test methodologies. There are other performance metrics that are important when choosing a TV, but most of the other metrics have more to do with the TV's electronics and processing than the panel.
Contrast
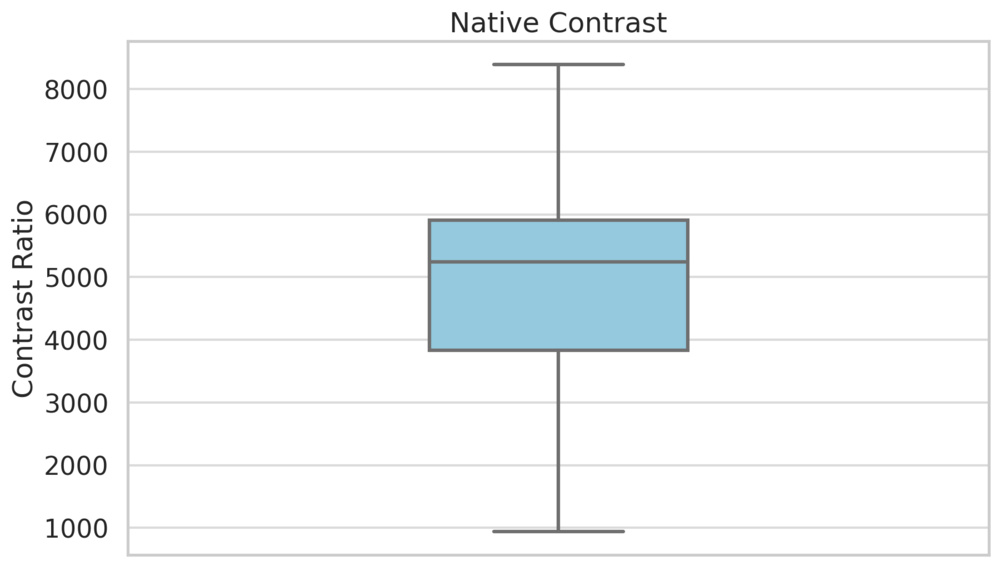
Contrast is one of the most important factors in TV picture quality, and we measure contrast in two different ways. Native contrast is the native contrast of the panel, with local dimming disabled. This shows us how well the TV performs in the most difficult scenes, where local dimming isn't precise enough to dim around the bright areas of the scene. In those complex scenes, the natural ability of the panel itself to block light is more important, so the performance depends on the specific type of LED panel used. VA panels tend to deliver the best native contrast results, while IPS or ADS panels are far worse. Read more about IPS vs VA.
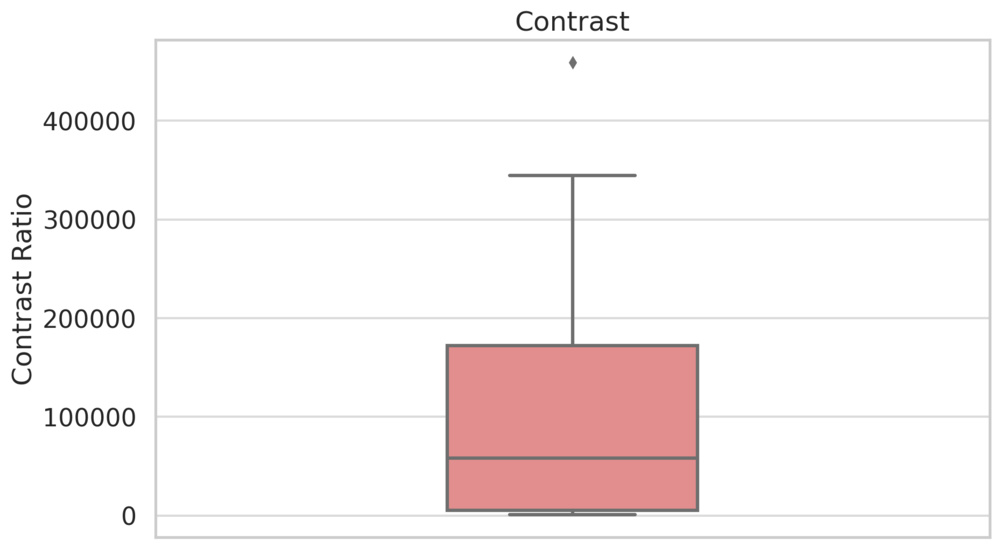
The contrast measurement shows the maximum contrast of the TV, with local dimming enabled. Here we can see that many LED TVs deliver truly spectacular contrast, mainly thanks to the latest Mini LED backlights that often have hundreds, if not thousands, of individual dimming zones. With good local dimming, the exact panel type isn't as important, and some of the TVs with the best local dimming contrast use ADS panels that have otherwise low native contrast. That's not to say that native contrast isn't important; it still is, but local dimming helps bridge the gap.
Brightness
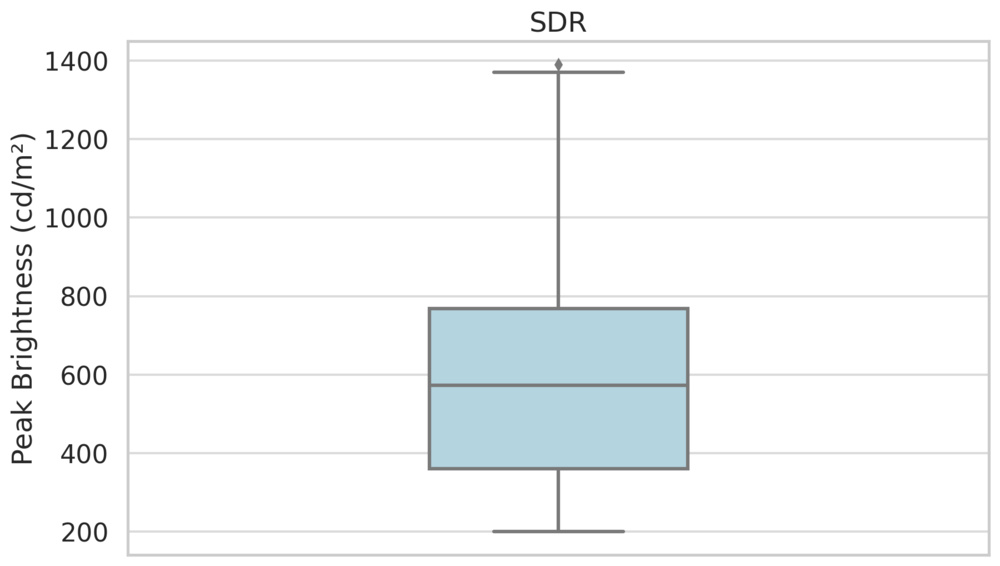
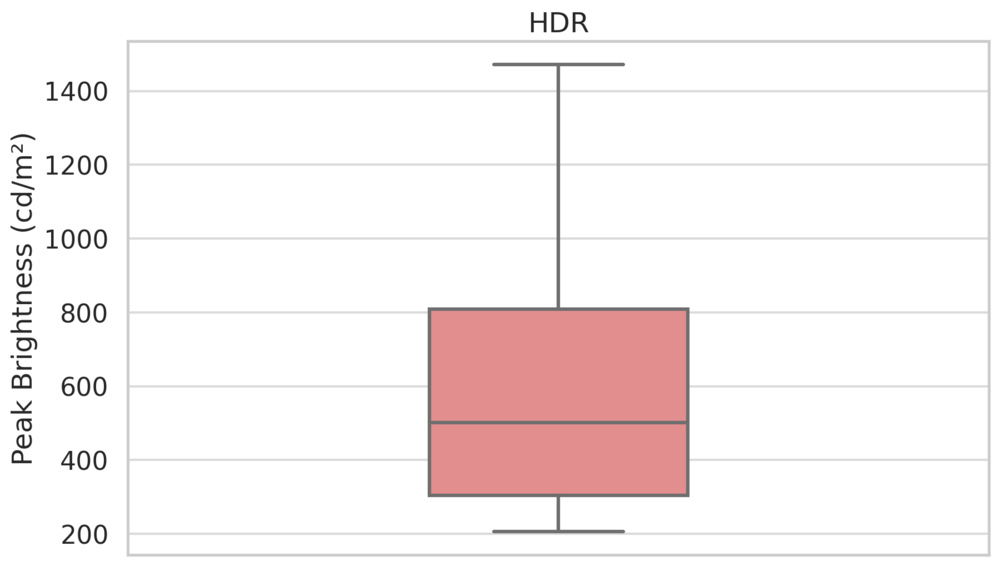
One of the core strengths of LED TVs is their incredible brightness. Even mid-range models in 2025 tend to have very good peak brightness, and you don't have to spend a lot to get a bright TV. High-end models are exceptionally bright, with some models even getting bright enough to be used outdoors in direct sunlight. LEDs also handle large, bright scenes well, with less of a drop-off in brightness as more of the screen is bright. This is important when watching sports or in overly bright outdoor shots in some movies and TV shows. Mini LED models are also able to redirect power to certain areas of the screen when needed, which is great if you have one part of the scene that's significantly brighter than the rest.
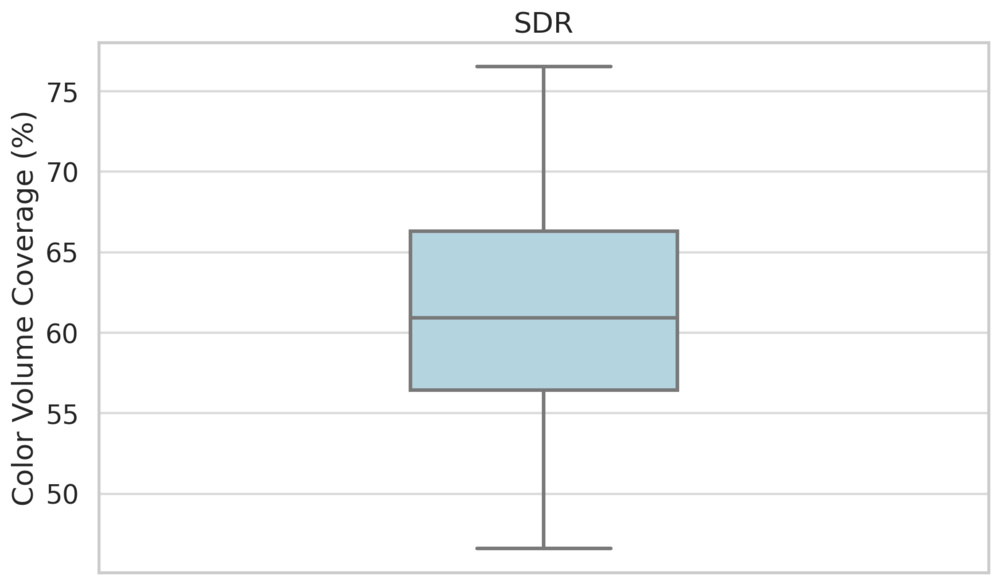
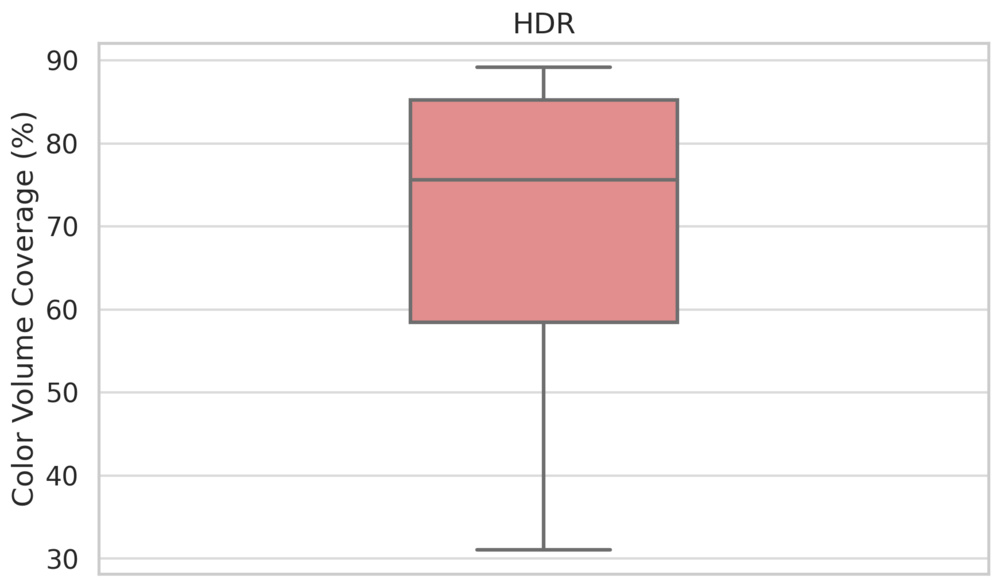
Color Volume
LED panels tend to have pretty good color volume. They achieve this through a combination of their high peak brightness and extra layers on the internal structure of the TV that improve color saturation. Many LED TVs make use of KSF phosphors or quantum dot colors to improve the range of colors they can produce. Combined with their typically good contrast ratios, especially on Mini LED models, most LED TVs are able to deliver a wide range of colors in both bright and dark scenes.
Motion Blur
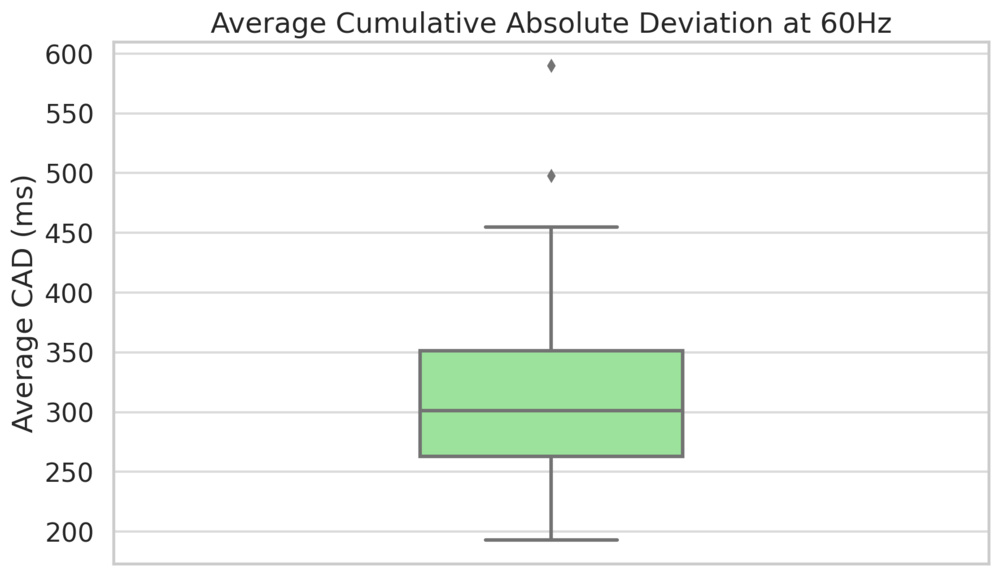
Unfortunately, one weak point with LED TVs is their overall response time. Like everything else on this list, it varies by individual model, but as you can see from the market performance chart, most LEDs have very high CAD values. This means that these panels take too long to transition from one shade to the next, so in faster action, you'll see a lot more blur. This extra motion blur is beneficial when watching movies as it reduces response time stutter, but it's not good for gaming or watching sports. The specific subtype of LED panel doesn't really matter when it comes to motion blur; there are good and bad models.
Conclusion
LED and LCD TVs are by far the most popular type of TV on the market, and for good reason. They deliver good picture quality overall and are available in an incredibly wide range of sizes and price points, so you're sure to find something that fits your needs and budget. Although the technology has been around for many years, it shows no signs of slowing down, and new and upcoming technologies like Micro LED and RGB Mini LED continue to push LED and LCD technology to new limits.